*02
CUBESATS
The New Space Revolution
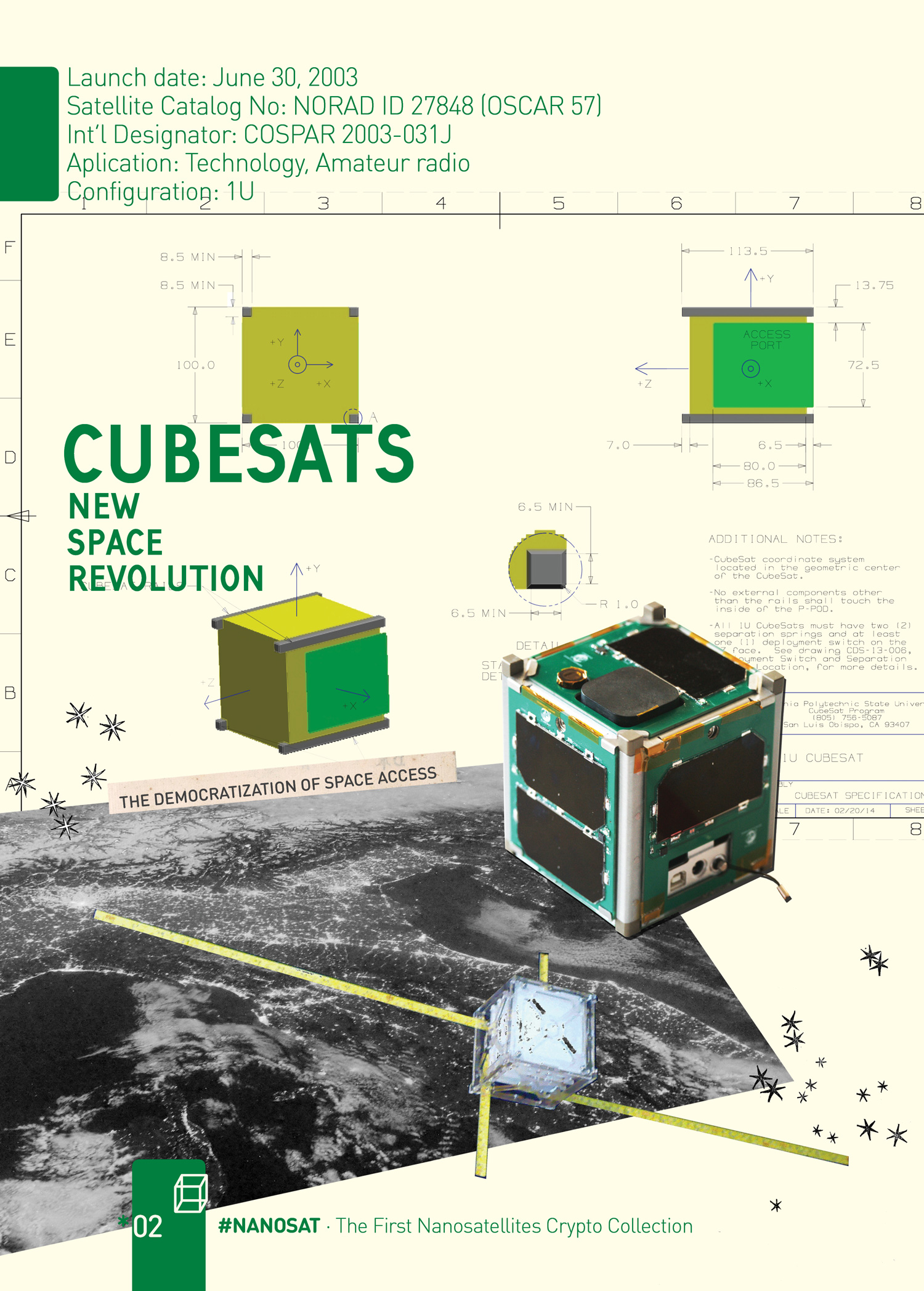
Recognized as a key piece of the New Space revolution, this tiny spacecrafts have revolutionized the Space Age, opening the democratization of space access, and challenging the traditional ways of space exploration. Created in 1999 by Bob Twiggs and Jordi Puig-Suari, CubeSat open-source standard is acclaimed today as the biggest thing in satellites since Sputnik! CubeSat spacecraft is a 10 cm cube with a mass of up to 1.33 kg, scalable from one to several units ("one unit" or "1U", 2U, 3U…) The first mission was a multiple launch of 6 CubeSats using a Rokot-KM rocket, a remake of the old SS-19 Stiletto soviet intercontinental ballistic missile. The CubeSats were: AAU-Cubesat Aalborg University Cubesat (DK), CanX 1 Canadian Advanced Nanospace eXperiments (CA), CUTE 1 CUbical Tokyo institute of technology Engineering satellite (JP), DTUSat Danmarks Tekniske Universitet Satellite (DK), QuakeSat (USA) and XI-IV (JP). One of them, the CubeSat XI-IV (Sai Four), the OSCAR 57, is still active. The name "XI" (X-factor Investigator) derives from its cubic shape (XI means domino in Japanese).
Launch date: June 30, 2003
Satellite Catalog No: NORAD ID 27848 (OSCAR 57)
Int'l Designator: COSPAR 2003-031J
Aplication: Technology, Amateur radio
Configuration: 1U
Tags: Space Nanosatellite CubeSat OpenSource COTS